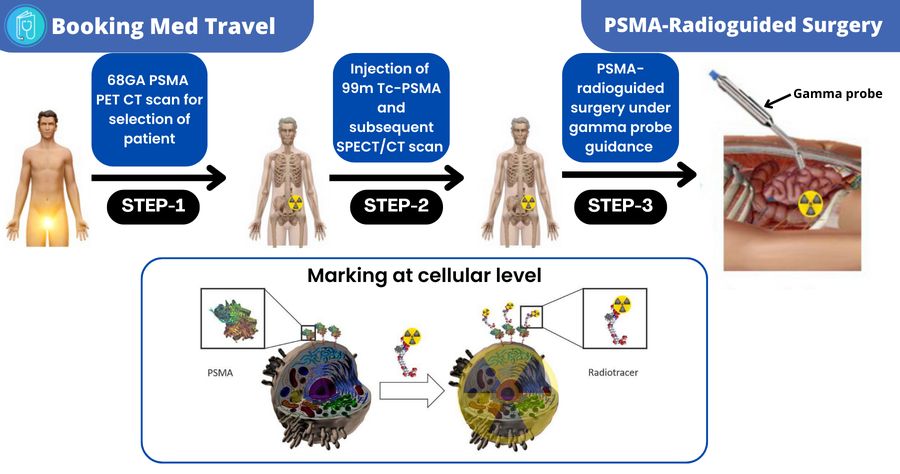
What is PSMA radioguided surgery?
PSMA radioguided surgery (PSMA-RGS) is the latest advancement, in the treatment of recurrent prostate cancer with metastasis to regional lymph nodes, that helps in the detection and targeted resection of cancer cells.
Preliminary results show that the PSMA radio-guidance technique is very sensitive and specific in tracking suspicious lesions intraoperatively.
The PSMA-RGS uses a special technique during which first the cancer cells are preoperatively marked with 99m Tc PSMA and a gamma probe is used intraoperatively to detect those marked cancer cells so that they can be easily removed.
How is PSMA radioguided surgery useful in recurrent prostate cancer with single lymph node metastasis?
Initially when the cancer cells leave the prostate gland and enter the lymphatic supply the only treatment that could be provided was long-term androgen deprivation therapy. However, the advancements have raised the possibility to treat the lymph node's metastasis with the help of salvage lymph node dissection (SLND) by PSMA-RGS
SLND not only delayed the spread of cancer but also increased the survival rate. It also saves the patient from the toxic and least effective systemic treatment. It is a relatively safe method for the treatment of prostate cancer for those who are in the oligometastatic stage.
What is a 68Ga PSMA PET-CT scan and how can it be useful?
During surgical resection or treatment of primary prostate cancer, some cancer cells escape the lesions or accidentally remain in the lesions which then set a stage for second malignancy.
The cancer cells are usually scattered in different locations which makes it difficult to detect these cells with normal screening, scanning, and diagnostics entities.
Positron emission tomography is currently the most widely used screening test that is available for the detection of cancerous cells based on their metabolic activity, blood flow, and physiology.
This technique uses radioactive substances also known as radiotracers to evaluate the functionality of the cells but even the most widely used tracer named radiolabeled choline derivative was unable to distinguish between different kind of cancer cells.
To overcome this problem 68Ga PSMA PET CT scan was developed which proved excellent and remarkable equipment in the detection of recurrent prostatic cancer.
In this technique, PSMA ligands with gallium68-labeled radiotracers are used to visualize even the smallest metastatic lesions having low PSA value with greater efficacy than usual routine X-rays and MRI scans.
This helps the physician to determine the exact size and location of the malignant tissue, making it easier to plan the surgical procedure.
Who are candidates for PSMA radioguided surgery?
In order to be a candidate for the surgery, the following criteria have to be fulfilled by the patient
- Having local recurrence of cancer with possible metastasis to lymph nodes
- Having good health with few other metabolic disorders and body syndromes
- Have the diagnosis of recurrent prostate cancer with positive 68 Ga-PSMA PET CT scan findings
- Having increased PSA value which is not too high as in primary prostate cancer but validates the recurrence.
How is the PSMA radioguided surgery performed?
After the initial assessment with 68Ga PSMA PET CT scan, the patient is referred for surgery where the following steps are taken
- The surgeon injects the 99m Tc PSMA into the patient’s body for the localization and marking of cancerous cells
- A SPECT scan is then performed to confirm 99m Tc-PSMA uptake in the same lesions as detected earlier by 68 Ga-PSMA PET CT scan
- The patient is then given general anesthesia.
- After administering the general anesthesia, the surgeon makes a small incision on the abdomen and pelvis through which a laparoscopic tube, a gamma probe, and a video camera are inserted.
- The gamma probe guides the surgeon to detect the marked metastatic cells present in different areas (such as metastatic lymph nodes) which are then easily removed by the surgeon
What happens during the follow-up after the surgery?
Follow-up of PSMA Radioguided surgery is important during which a PSMA PET CT scan is performed to make sure that there are no cancerous cells remaining in the body of the patient and also to detect recurrence in any other area.
The patient is also advised to check PSA levels at regular intervals
Prognosis
Gamma probes help in exact measurements of the lesions for their complete resection with a specificity of more than 95%.
What are the latest advancements in PSMA radioguided surgery?
Gamma probe guidance has made the PSMA radio-guided surgery successful by increasing the survival rate of patients with prostatic cancer with loco-regional metastasis.
Firstly conventional gamma probes were used but nowadays DROP-IN gamma probes are administered during robot-assisted laparoscopic surgery which has increased the success rate even more.
Future perspectives
By taking into account the prevalence of prostatic cancer it is essential to do advancements to treat prostatic cancer. The PSMA radioguided surgery is the latest invention that was developed in Germany but now it is increasingly employed to detect and resect metastatic lymph nodes. Currently, the procedure is only available in 2 centers in Germany (i.e. Martini Klinik in Hamburg and University hospital Rechts der Isar in Munich) but doctors are trying to extend this procedure to an increasing number of specialized centers so that more patients can benefit from it.
Cost of PSMA radioguided surgery in Germany
PSMA radioguided surgery has been developed in Germany and currently, the procedure is only available in 2 centers in Germany i.e. Martini Klinik in Hamburg and University hospital Rechts der Isar in Munich. The cost of the surgery ranges between 20,000-32,000 Euros. This amount covers the cost of the initial clinical and laboratory examination, the PSMA-RGS itself, the follow-up examinations, the hospital stay, and the elaboration of recommendations for future treatment.


Comments